tests to use in physical therapy to diagnosis rtc tear|full thickness tear test : warehouse Based on the Park et alstudy, the combination of the following 3 special tests have produced the highest post-test probability to diagnose a full-thickness rotator cuff tear: 1. The Drop . See more webWatch Beta porn videos for free, here on Pornhub.com. Discover the growing collection of high quality Most Relevant XXX movies and clips. No other sex tube is more popular and .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Grátis para mobile e TV. Aplicativo para quem quer integrar os canais ao Live Channels e/ou ao menu da televisão. Ele permite transformar grupos da lista original em categorias do Live Channels. Televizo ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ A versão grátis para mobile e TV tem os recursos mais relevantes, sendo um ótimo aplicativo mesmo para quem não tem .
To test the presence of a shoulder full-thickness rotator cuff tear using the Drop-Arm Sign, Painful Arc Sign, and the Infraspinatus Muscle Test. See more
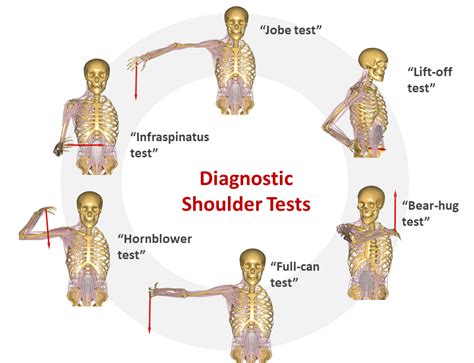
Based on the Park et alstudy, the combination of the following 3 special tests have produced the highest post-test probability to diagnose a full-thickness rotator cuff tear: 1. The Drop . See moreThe Drop-Arm Sign Patient actively elevates the arm in the scapular plane and then slowly reverses the motion. A positive test is defined as the patient experiencing pain during the . See more
Special testing is generally performed following a full examination of the shoulder that includes but is not limited to patient history, mechanism of injury, clinical observation, bony and soft tissue palpation, assessment of active and passive .
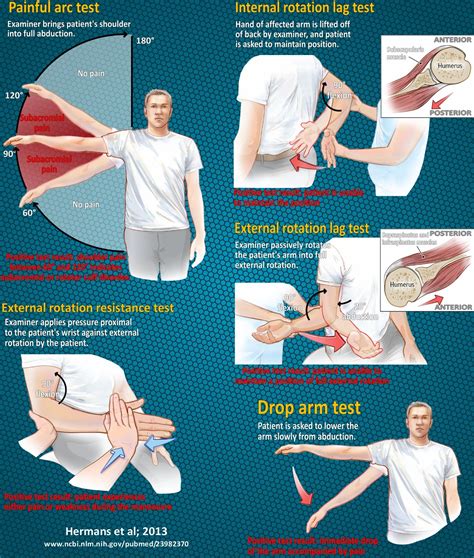
Physical examination is extremely important to evaluate the presence, location, and extent of a tear. It also helps us to understand the mechanism of pain. Conservative .The diagnosis of a rotator cuff tear can be established by a careful history and a structured physical examination. The physical examination should include inspection and palpation, range of motion testing, strength testing and . The best combination of tests to detect a full-thickness RTC tear are a positive painful arc test, drop-arm test, and infraspinatus muscle weakness test. Further research is needed to differentiate partial RTC tears .
Overview. This guideline provides recommendations on the management of patients with rotator cuff tears. Get The CPG. Members Only Content. Join APTA to get . Rotator cuff tears are one of the most common injuries we see in orthopedic physical therapy. During the clinical examination of the shoulder, we want to perform special tests designed to detect a rotator cuff tear. A doctor or physiotherapist can use one of more than 25 functional tests during a physical exam to diagnosis a torn rotator cuff. Some of these tests directly indicate a rotator cuff injury and.
Imaging tests may include: X-rays. Although a rotator cuff tear won't show up on an X-ray, this test can visualize bone spurs or other potential causes for your pain — such as . The best combination of tests to detect a full-thickness RTC tear are a positive painful arc test, drop-arm test, and infraspinatus muscle weakness test. Further research is needed to differentiate partial RTC tears from full . Introduction. Rotator cuff (RTC) pathologies are responsible for nearly 4.5 million healthcare visits per year, with tears affecting approximately 30% of adults over the age of 60 and 62% of those over the age of 80 [1-3].The unadjusted volume of all RTC repairs increased by 141% between 1996 and 2006 [].]. With the continually aging population, the incidence of tears . More commonly, rotator cuff tears occur over time as your tendon wears down with age and use (degenerative tear). People over age 40 are most at risk. Causes of degenerative tears include: Bone spurs: Bony growths can form on the top of your shoulder bone. These bone spurs rub against your tendon when you lift your arm.
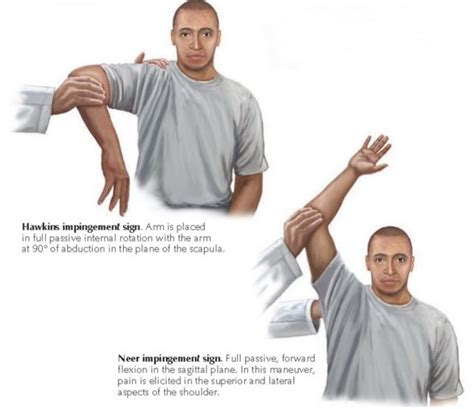
Chen CW, Pan ZE, Zhang C, Liu CL, Chen L. [Clinical research on the efficiency of physical examinations used for diagnosis of subacromial impingement syndrome]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2016;29(5):434-8.. Guosheng Y, Chongxi R, Guoqing C, Junling X, Hailong J. The diagnostic value of a modified Neer test in identifying subacromial impingement syndrome. Physical examination. Physical examination starts with inspection. It is easy to detect muscle atrophy of the infraspinatus viewing from the back of the patient because the infraspinatus is located just under the skin, whereas the supraspinatus is covered by the trapezius (Fig. 1).Atrophy of the shoulder muscles is a common finding in patients with rotator cuff tears.
torn rotator cuff tendon physical exam
How is Rotator Cuff Tear Diagnosed? Some of the tests a physician may use to help diagnose a Rotator Cuff Tear include: Physical examination with complete evaluation of medical history; X-rays: X-rays use radiation to produce images of the shoulder. This can help your physician rule-out other possible causes for shoulder discomfort, such as a . The diagnosis of rotator cuff tendinitis or tear is usually based upon a careful medical history, the person's symptoms, and a physical examination. Again, as inflammation is seldom involved in these injuries, particularly if more than 36 hours have passed since the inciting event, most experts prefer the terms "tendinopathy" or "tendinosis" to .The sensitivity of belly-press test in the diagnosis subscapularis muscls tear is 0.34 and specificity is 0.96. If only grade 2-4 tears were analyzed the sensitivity was 0.37 and specificity was 0.92. The study by Angela Cadogan et al found that the belly-press test demonstrated acceptable level of inter-examiner reliability.The diagnostic accuracy of special tests for rotator cuff tear: the ROW cohort study. American journal of physical medicine & rehabilitation. 2017 Mar;96(3):176. ↑ Lädermann A, Meynard T, Denard PJ, Ibrahim M, Saffarini M, Collin P. Reliable diagnosis of posterosuperior rotator cuff tears requires a combination of clinical tests.
elephone s7 drop test
(Level 1 study: Evidence that physical therapy is an effective treatment for atraumatic full-thickness RTC tears in 2 year follow-up.) Koh, KH, Kang, KC, Lim, TK, Shon, MS, Yoo, JC.Special tests with reported data for rotator cuff tears that fail to consistently meet the diagnostic threshold for use in this study included the empty can test, 9,12.16,19,20,21 the full can test, 21 the Neer test, 9,13 the Hawkins-Kennedy test, 9,13 the Rent test, 22,23 the Gilcrest palm-up test, 9,12,18 drop sign in 90 degrees abduction in .
Synopsis “Special tests” for rotator cuff–related shoulder pain (RCRSP) have passed their sell-by date. In this Viewpoint, we outline fundamental flaws in the validity of these tests and their proposed ability to accurately identify a pathoanatomical source of pain. The potential harm of these special tests comes in conjunction with imaging findings that are .
fda drop ball impact resistance test 804.410
tear in rotator cuff test
Evidence [edit | edit source]. The infraspinatus test showed a high sensitivity of 0.90 and specificity of 0.74. Test Item Cluster: This test may be combined as a cluster with the Hawkins-Kennedy Impingement Sign and the Painful Arc sign to test for subacromial impingement.If all three tests report a positive, then the positive likelihood ratio is 10.56 and if all three tests are . Rotator cuff tears are a very common source of shoulder pain and decreased motion that can occur due to both traumatic injuries in young patients as well as degenerative disease in the elderly patient. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with provocative tests of the supraspinatous, infraspinatous, teres minor and subscapularis, but .Your doctor will likely order one or more of the following advanced imaging tests to diagnose a rotator cuff tear and determine the extent of the damage: X-ray; MRI; Musculoskeletal ultrasound; . Physical therapy; If non-invasive .
APTA: Physical Therapist Management of Glenohumeral Joint Osteoarthritis Clinical Practice Guideline (CPG+) Apr 28, 2023 . This guideline was created by an American Physical Therapy Association volunteer guideline development group and covers clinical information and accepted
The rotator cuff is an anatomic coalescence of the muscle bellies and tendons of the supraspinatus (SS), infraspinatus (IS), teres minor (TM), and subscapularis (SubSc) surrounding the shoulder joint (see Image. Shoulder . Injuries to the rotator cuff (RC) range from simple contusions and tendonitis to chronic tendinopathy, partial tears, and full-thickness tears (PTTs versus FTTs). RC pathology can affect any subset of patient populations, from the casual “weekend warrior” to elite-level professional athletes. Similarly, RC pathology is seen across all ages.[1][2] Synopsis The hallmark characteristics of rotator cuff (RC) tendinopathy are pain and weakness, experienced most commonly during shoulder external rotation and elevation. Assessment is complicated by nonspecific clinical tests and the poor correlation between structural failure and symptoms. As such, diagnosis is best reached by exclusion of other .
Physical Therapy Management . Physical therapy of rotator cuff problems aims to reduce pain and swelling of the tendons, to achieve normal range of motion and eventually strengthen the shoulder. Initially rest and ice are used to decrease pain. It’s very important that patients initially avoid activities that increase pain and symptoms.
The aim was to assess diagnostic accuracy of 15 shoulder special tests for rotator cuff tears. From 02/2011 to 12/2012, 208 participants with shoulder pain were recruited in a cohort study. Among tests for supraspinatus tears, Jobe’s test had a . Purpose of Review This paper should serve as a guide for nonoperative physicians in the management of rotator cuff tears and provide an algorithm of when to refer patients for potential operative repair. Recent Findings While physical therapy remains the mainstay of conservative treatment, recent studies have examined various injections to improve pain and .
A Wilcoxon signed rank test with continuity correction was used to compare initial, 6 week, and 12 week outcome scores. . decided to conduct a prospective cohort study on the non-operative treatment of atraumatic full thickness rotator cuff tears using the physical therapy protocol derived from . however those that had pain or functional . Physical therapy is a great option to consider, as early intervention and treatment can keep someone with a torn rotator cuff out of the operating room. It can also reduce or even prevent the need for long-term medications and cortisone shots to treat the injury and pain. 5. The Yocum test featured 78% sensitivity and 96% specificity. 6. The Patte test featured 38% sensitivity and 98% specificity. 7. The drop arm test for supraspinatus featured 53% sensitivity and 82% specificity—and was the most specific for full-thickness rotator cuff tears. 3. There are several tests for that assess the other structures .How to Use Special Tests. The performance of special tests with the intention of diagnosing or providing treatment recommendations for someone experiencing symptoms should be performed only by a licensed medical professional such as a PT, OT, medical doctor or athletic trainer. Clinicians who perform special tests may use the data for:
rotator cuff tear physical exam
Rest: Taking a break from physical activity — especially the sport or activity that caused the impingement. Physical therapy: A physical therapist will give you stretches and exercises to strengthen your shoulder and improve its range of motion. As your shoulder heals, they’ll give you exercises to strengthen the muscles in your rotator cuff.
- Você me ama? Perguntou Alice - Não, não te amo! Respondeu o coelho branco. Alice enrrugou a testa e cruzou os braços, da mesma forma quando se sentia ferida. - Viu, Alice! Disse o coelho Agora vais começar a perguntar o que te torna tão imperfeita e o que tu fez de errado para que eu não consiga te amar, nem que seja um pouco.
tests to use in physical therapy to diagnosis rtc tear|full thickness tear test